This article contains information on Problem Solving as a Teaching Strategy.

Education sharpens various areas of our lives. Education is expected to produce the workforce who have the capability to solve problems and make innovation. This expectations can not be met without a teacher who is well trained and knows the strategies to employ when teaching.
There are different teaching methods and strategies, it is upto the teacher to know which strategy works best in order to carry every member of the class along. In this article, we will be looking at an important teaching strategy that every educator should consider at intervals which is Problem solving strategy.
Application of problem-solving as a teaching strategy by educators is another means of producing problem solvers and innovators at the workplace.
What is Problem Solving?
Problem-solving is a process of identifying, analyzing, and resolving problems.
What is Problem Solving Teaching Method?
Problem solving teaching method [2] is a child centered approach of teaching that prioritizes active learning and critical thinking skills. It involves presenting students with real-world problems that they must solve and guiding them through collaboration, analysis and critical thinking.
This method fosters higher-order thinking, collaborative skills, and the development of problem-solving strategies that can be applied across various cases. By engaging students in real problem-solving experiences, this teaching method promotes deep understanding, relevance, and transferability of knowledge and skills.
However, it is important to consider potential challenges and limitations associated with this approach.
Steps To Problem Solving as a Teaching Method
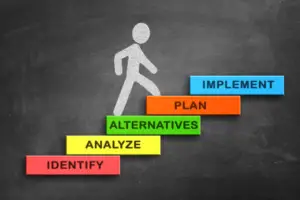
The process of problem solving as a teaching method typically involves several steps [1] which includes the following:
1. Problem Identification
There can never be a solution when there is no visible problem. The first step in this teaching approach is identifying the problem. Here, the teacher presents a problem that is relevant to the subject matter being taught. The problem should be challenging enough to require students to think critically and apply their knowledge and skills.
2. Analysis and Understanding
Haven identified the problem, students are encouraged to carefully analyze and understand the problem by breaking it down into different parts. Here, they may need to identify relevant information, define key terms, and determine the relationships between different elements of the problem.
3. Developing Strategies
At this stage students brainstorm and generate strategies or approaches to solve the problem. This step encourages creativity and critical thinking, as students explore different avenues for finding a solution.
4. Planning and Execution
Like the saying goes, a plan remains a mere dream if it has not been executed. This same is applicable in problem solving. At this phase of the teaching strategy,
students select the most appropriate strategy (plan) or combination of strategies and develop a plan to implement it. They consider the steps they need to take, the resources required, and any potential challenges they may encounter.
5. Application and Evaluation
This is the last stage of problem solving. Here, students apply their chosen strategy to solve the problem. This step involves carrying out the plan, making adjustments when and where necessary, and evaluating the effectiveness of the chosen approach.
These are the various processes the problem solving teaching strategy exposes students to.
Advantages/Benefits of the Problem Solving Teaching Strategy.
Problem solving as a teaching method offers several benefits [3]. Here are some of them.
1. Active Learning

In this teaching approach, all hands are on deck. Students actively engage with the subject matter, which enhances their understanding. They are not passive recipients of information but become active participants in the learning process because the solution to a problem must be found.
2. Transferable Skills
In this teaching approach, students learn to think deeply, consider multiple perspectives, and make informed decisions based on evidence and logical reasoning.
Hence, the problem-solving process also equips students with skills that can be applied in various domains and situations beyond the classroom. These skills include analytical thinking, creativity, communication, collaboration, and resilience in the face of challenges.
3. Real-World Relevance
By presenting realistic problems, students can see the direct importance of what they are learning when it can be related to real-life situations. This increases motivation and engagement, as they understand the practical applications of their knowledge and skills.
4. Collaboration and Communication
Problem solving often involves collaboration among students. They learn to work together, share ideas, and communicate effectively to arrive at a solution. This fosters teamwork and interpersonal skills and healthy relationship among the students.
Disadvantages of Problem Solving Teaching Strategy
While problem-solving as a teaching method has numerous benefits, it is important to note the potential disadvantages as well. Here are some challenges associated with this approach:
1. Time Constraints
Implementing problem-solving activities requires time for students to engage in critical thinking and collaboration. This can be challenging especially in cases of a packed curriculum and limited instructional time.
2. Assessment Difficulties
Traditional assessment methods, such as standardized tests, may not effectively capture the full range of skills and knowledge developed through problem-solving activities. Assessing students’ problem-solving abilities often requires alternative assessment approaches, such as performance assessments or rubrics that evaluate their process and thinking rather than just the final answer which is the case with the traditional method of assessment.
3. Unequal Participation
In collaborative problem-solving activities, there is a risk of some students dominating the discussions while others may become passive observers. Teachers need to actively promote equal participation and ensure that all students have a voice and contribute meaningfully in the process.
4. Frustration and Discomfort
Engaging in problem-solving can be challenging and may lead to frustration or discomfort for some students. The ambiguity and open-ended nature of problems can create anxiety, especially for students who prefer structured tasks or have a fear of failure. Therefore, teachers must create a safe learning environment to address these concerns if this teaching approach must be adopted.
5. Teacher Expertise
Effective implementation of problem-solving as a teaching method requires teachers to have a strong understanding of the subject matter and the ability to facilitate the problem-solving process. Some teachers may require additional training and support to effectively guide students through complex problems and not all schools may have the capacity to see that these conditions are met.
6. Resource Requirements
Certain problem-solving activities may require specific resources, materials, or technology. Limited access to these resources can pose challenges in implementing problem-solving as a teaching method, particularly in resource-constrained environments. This teaching strategy can be said to be cost intensive cmwhich can be a challenge to some institutions.
Despite these challenges, problem-solving as a teaching method remains a valuable approach to enhance critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. By addressing these disadvantages proactively, teachers can maximize the benefits and create a supportive learning environment for students.
Conclusion
Problem solving as a teaching method is an effectit teaching strategy that promotes active learning, critical thinking and collaboration among students. By engaging with real-world problems, students develop skills that extend beyond the classroom and into other aspects of their lives. However, challenges such as time constraints, assessment difficulties, unequal participation, student frustration, teacher expertise, and resource requirements must be considered and addressed before this method is adopted.
Despite these challenges, with thoughtful implementation, problem solving as a teaching method can empower students to become effective problem solvers and critical thinkers which are skills that will make them standout amongst their contemporaries even in the work force. By fostering a supportive learning environment, and encouraging reflection, teachers can maximize the potential of problem solving as a powerful educational tool.
References
[1] “8-Step Problem Solving Process.” University Human Resources – The University of Iowa, https://hr.uiowa.edu/development/organizational-development/lean/8-step-problem-solving-process.
[2] Hoque, Ekramul. “Problem-Solving Method in Teaching.” EduCere Centre, 22 Feb. 2022, https://educerecentre.com/problem-solving-method-in-teaching/?utm_content=expand_article.
[3] Sherman, Fraser. “Advantages and Disadvantages of Problem-Based Learning in the Workplace.” Work – Chron.com, Chron.com, 28 June 2013, https://work.chron.com/advantages-disadvantages-problembased-learning-workplace-22868.html.
Don’t miss out on current updates, kindly like us on Facebook & follow us on Follow @EAfinder OR leave a comment below for further inquiries.






